#GS1 barcode validation
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
GTIN-12
What is GTIN-12 and How Does it Work?
In today’s fast-paced retail and supply chain industries, effective product identification is key to ensuring smooth operations. One of the most widely used product identification systems is the GTIN-12, also known as the Universal Product Code (UPC). The GTIN-12 plays a crucial role in improving product tracking, inventory management, and consumer transactions. It is recognized globally and serves as the standard for identifying individual products, particularly in North America.
What is GTIN-12?
The GTIN-12 is a 12-digit number used to uniquely identify products at the retail level. It is part of the larger Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) system, which is managed by GS1, the global organization responsible for product identification standards. The GTIN-12, commonly referred to as the UPC (Universal Product Code), is one of the most widely recognized and used barcodes in the world.
Each GTIN-12 is unique to a specific product or service and is typically encoded into a barcode that can be scanned at various points along the supply chain, from warehouses to point-of-sale systems.
Structure of GTIN-12
The GTIN-12 consists of 12 digits, each of which serves a specific purpose. Here is a breakdown of its structure:
Company Prefix: The first set of digits, typically between 6 to 10 digits, is assigned to a company or manufacturer by GS1. This prefix identifies the company that owns the product and is a unique identifier for the manufacturer.
Item Reference: The next set of digits represents the product or item. These digits are unique to the specific product or SKU, helping to differentiate it from other products produced by the same manufacturer.
Check Digit: The final digit is the check digit, calculated using a mathematical formula to ensure that the GTIN-12 number is correctly formatted. It acts as a validation tool, helping to detect errors in scanning or data entry.
How Does GTIN-12 Work?
The GTIN-12 is encoded into a barcode, which is printed on the product packaging. When scanned, the barcode is decoded, and the corresponding product information is retrieved from a database, such as price, description, stock levels, and more.
Here’s a simple example of how the GTIN-12 works in a retail setting:
Product Creation: A manufacturer produces a product, such as a bottle of shampoo. The manufacturer registers with GS1 and is assigned a company prefix. They then create a unique GTIN-12 for each variation of the product (e.g., size, color, or packaging).
Barcode Generation: The GTIN-12 number is then encoded into a barcode, which is printed on the product’s packaging.
Scanning and Data Retrieval: At the point of sale, a cashier scans the GTIN-12 barcode on the shampoo bottle. The barcode scanner decodes the GTIN-12, and the relevant product information (such as price and description) is displayed in the store’s system, allowing the transaction to be completed efficiently.
Benefits of GTIN-12
Improved Efficiency: The GTIN-12 allows for quick and accurate product identification using barcode scanners. This speeds up the checkout process, reduces manual errors, and streamlines inventory management.
Standardization: The GTIN-12 is recognized globally and follows the same format, making it easy for businesses to identify products across various regions. For example, retailers in North America widely use GTIN-12 barcodes, making it easy to trade and distribute goods internationally.
Reduced Errors: By eliminating the need for manual entry of product details, GTIN-12 reduces the risk of human error, ensuring that the correct product is scanned, purchased, and shipped.
Better Inventory Control: With GTIN-12 barcodes, businesses can track product sales and stock levels in real-time. This helps retailers and suppliers make informed decisions about restocking, reducing inventory costs, and preventing stockouts.
Enhanced Consumer Experience: The GTIN-12 simplifies the checkout process for consumers. Barcode scanning ensures fast and accurate transactions, leading to a better shopping experience.
E-commerce Compatibility: Many e-commerce platforms, including Amazon, require products to have a GTIN-12 for listing. Having a unique GTIN-12 for each product enables businesses to sell their items on various online marketplaces, increasing visibility and sales.
When Should You Use GTIN-12?
The GTIN-12 is primarily used for individual products, especially in North America. Retailers and wholesalers often rely on GTIN-12 to track items on store shelves or manage inventory at a distribution center. GTIN-12 is suitable for products that are sold individually or in standard retail packaging.
Here are some examples of when you should use GTIN-12:
Retail Products: GTIN-12 is widely used for everyday products, such as groceries, clothing, electronics, and personal care items, sold at retail stores.
E-commerce: If you sell products online, many platforms require a GTIN-12 to list your items and ensure accurate product identification.
Manufacturers and Distributors: Manufacturers producing consumer goods or products for sale to distributors often use GTIN-12 to uniquely identify their products for resale.
How to Obtain a GTIN-12
To obtain a GTIN-12, businesses must first register with GS1, the organization responsible for assigning GTINs. Once registered, GS1 will assign the company a unique company prefix, which is used to generate GTIN-12 numbers for the products. Businesses will then create barcodes that correspond to each GTIN-12 and attach them to their products.
If you're new to the process and need help with generating GTIN-12 barcodes, resources like gtin.info can guide you through the process.
Conclusion
The GTIN-12 (UPC) is a crucial element of the GTIN system that plays a significant role in product identification, inventory management, and retail operations. Whether for streamlining transactions, improving stock tracking, or enabling e-commerce sales, GTIN-12 provides businesses with an efficient, standardized system for managing products. By adopting GTIN-12, companies can ensure smoother operations, reduce errors, and enhance the overall customer experience. For businesses looking to implement GTIN-12, resources like gtin.info provide valuable information and support to help you get started.
0 notes
Text
barcode-us.info
Barcode-us.info appears to be a website that provides services related to obtaining barcodes, including UPC (Universal Product Code) and GTIN (Global Trade Item Number) barcodes. These types of barcodes are essential for businesses, particularly those in retail, to uniquely identify products, streamline sales transactions, and manage inventory efficiently.
While I cannot access specific websites, it’s likely that barcode-us.info offers the following services based on general practices:
Common Services Offered by Barcode Websites (like barcode-us.info):
Obtain UPC/GTIN Barcodes:
The website may allow businesses to purchase UPC or GTIN barcodes for their products, which are necessary for listing items in retail stores, e-commerce platforms, or any marketplace that requires product identification.
Barcode Registration:
Some websites help businesses register their barcodes with GS1 (the official global organization that manages barcode standards), ensuring that each barcode is unique and compliant with industry standards.
Barcode Generation:
The site might offer tools to generate barcodes for your products once you've been assigned a unique GTIN or UPC code. These barcodes can then be used for labeling and tracking products.
Barcode Validation:
It’s crucial that barcodes are properly formatted and scannable. Websites like barcode-us.info may offer tools to validate your barcodes to ensure they are correctly generated and can be scanned easily.
Barcode Printing:
The website might also assist with the printing of your barcodes or offer guidance on how to print them yourself in a scannable format on product labels or packaging.
Support and Consultation:
If you're new to barcodes, they may offer consulting services or customer support to guide you through the process of obtaining and using barcodes effectively.
Why You Might Need a Barcode:
Retail Transactions: A barcode is essential for retailers to scan and track products during sales transactions.
Inventory Management: Barcodes make it easier to manage stock levels, track products, and streamline supply chain operations.
E-commerce: Online marketplaces like Amazon, eBay, and Walmart require UPC or GTIN barcodes for product listings.
Global Standards: Barcodes allow products to be identified globally, ensuring that they meet international standards for product identification and traceability.
Things to Check Before Using Barcode Services:
Official GS1 Registration: Ensure the website is offering valid GS1 barcodes. GS1 is the authorized organization that issues official barcodes.
Pricing: Check for hidden fees or annual renewal charges when registering barcodes.
Support: Ensure that the website offers adequate customer support in case you need help with generating or using barcodes.
If you’re considering using barcode-us.info, make sure to research the website and verify its legitimacy before purchasing any barcodes to ensure you're getting the right service for your business needs.
0 notes
Text
upc barcode
The Power of UPC Barcodes: Revolutionizing Retail and E-commerce
In the modern world of retail, efficiency and accuracy are key to ensuring smooth transactions, proper inventory management, and excellent customer service. One of the most powerful tools in achieving this is the UPC barcode—a 12-digit code that serves as the backbone of product identification in many sectors.
This article will explore what UPC barcodes are, how they work, and why they are essential for businesses and consumers alike.
What is a UPC Barcode?
A UPC barcode is a type of barcode that represents the Universal Product Code (UPC). It is a 12-digit numerical code used to uniquely identify products in retail environments. The code is visually represented by a series of black and white bars, which can be scanned using barcode scanners. These scanners read the pattern and convert it into digital information, allowing systems to retrieve detailed product data instantly.
While the UPC refers to the numerical code itself, the UPC barcode is the graphical representation that can be scanned, making the process automated and fast.
How Does a UPC Barcode Work?
The UPC barcode is made up of several key components:
The First Digit: This digit signifies the type of product. For example, a "0" often means a standard product, while other digits can refer to specific categories like pharmaceuticals or books.
Manufacturer Code: The next six digits identify the manufacturer or company responsible for the product. These are assigned by a global organization called GS1.
Product Code: The next five digits represent the specific item being sold, ensuring each product has a unique identifier.
Check Digit: The last digit is a check number used for error detection. This ensures the barcode is correctly scanned and validated.
Together, these components enable retailers to scan the UPC barcode, retrieve the corresponding product data (e.g., price, description, stock levels), and update the inventory system.
The Importance of UPC Barcodes in Retail
Faster Checkout Process: The most obvious benefit of UPC barcodes is the speed they bring to the checkout process. By simply scanning the barcode, cashiers can instantly pull up product information and prices. This saves time and reduces human error compared to manually entering prices.
Inventory Management: UPC barcodes play a crucial role in inventory management. Scanning the barcodes during purchases or stock checks automatically updates inventory counts in real-time. This helps businesses maintain accurate stock levels, prevent overstocking or stockouts, and optimize product ordering.
Price Accuracy: With UPC barcodes linked directly to a pricing database, the risk of pricing errors at checkout is minimized. This ensures that the correct price is charged for each product, which is important for customer satisfaction and business integrity.
Improved Efficiency Across the Supply Chain: The use of UPC barcodes streamlines operations not only in retail but throughout the entire supply chain, from manufacturers to distributors and retailers. It enables seamless tracking of products and facilitates faster shipping and receiving of goods.
Global Standardization: While different countries may use slightly different systems, the UPC barcode format is globally recognized and compatible with other international barcode systems such as the EAN (European Article Number). This standardization allows products to be tracked easily across international borders, benefiting both businesses and consumers in the global marketplace.
How to Create a UPC Barcode
Creating a UPC barcode for your products involves a few important steps:
Join GS1: GS1 is the global authority responsible for assigning UPC codes. As a business, you’ll need to register with GS1 to get a unique manufacturer identification number. This number forms part of the UPC barcode.
Assign UPC Codes to Your Products: Once you have your manufacturer number, you can begin assigning unique product identifiers to your items. Each product, regardless of size, color, or type, should have its own UPC barcode.
Generate the Barcode: After you’ve assigned UPC codes, you can convert them into barcode format. Many GS1-approved barcode generation tools can help create the correct barcode image, which you can print and apply to your products.
Test the Barcode: Before applying the barcode to your products, it’s important to test it to ensure it’s scannable and works properly in various retail environments.
Challenges and Misconceptions About UPC Barcodes
UPC Barcodes Are Only for Physical Products: While UPC barcodes are most commonly used in physical retail stores, they are also used in e-commerce. Online platforms require UPC codes to list products, and UPCs help with inventory management and order fulfillment.
UPC vs. QR Code: While both UPC barcodes and QR codes are used to store information, they serve different purposes. UPC barcodes are designed for product identification in retail settings, while QR codes are more versatile and can store more diverse information, including links, promotions, and contact details.
Global Compatibility Issues: Although UPC barcodes are widely used in the United States and Canada, other countries may use different systems, such as EAN. However, the UPC and EAN systems are generally compatible, and many barcode scanners can read both types.
Conclusion
The UPC barcode is a vital tool in today’s retail and e-commerce industries, making transactions faster, inventory management more accurate, and global trade more efficient. By providing a simple yet effective way to identify products, UPC barcodes have revolutionized the way businesses and consumers interact with products on a daily basis.
For any business owner looking to expand their reach, adopting UPC barcodes is crucial for maintaining smooth operations, improving customer experiences, and ensuring product traceability across the globe. Whether in physical stores or online marketplaces, UPC barcodes will continue to be an essential component of modern retail.
0 notes
Text
upc
Understanding UPC: The Universal Product Code Explained
The Universal Product Code (UPC) is a standardized barcode system used globally for tracking and identifying products in retail and supply chains. Since its introduction in the early 1970s, UPC has become an essential tool for streamlining sales processes, improving inventory management, and reducing human errors in retail operations. In this article, we will explore what UPC is, how it works, and why it remains a cornerstone of modern commerce.
What is a UPC?
A Universal Product Code (UPC) is a 12-digit numeric code accompanied by a machine-readable barcode. It is used to uniquely identify products in stores, warehouses, and throughout the supply chain. The UPC serves two main purposes:
Product Identification: Each UPC is tied to a specific product and manufacturer, ensuring accurate identification during sales transactions.
Efficient Scanning: The barcode allows cashiers and inventory systems to quickly retrieve product information, including price, description, and stock levels.
The UPC system was first introduced in 1974 by the Uniform Code Council (UCC) (now known as GS1 US). The adoption of UPC codes revolutionized retail operations by replacing manual price entry with fast, accurate barcode scanning.
Structure of a UPC Code
A standard UPC-A barcode consists of 12 digits, divided into three key parts:
Company Prefix (First 6 digits): Assigned to manufacturers by GS1, this identifies the company producing the product.
Item Reference Number (Next 5 digits): Assigned by the manufacturer, this uniquely identifies the specific product.
Check Digit (Last digit): A calculated number used to verify the accuracy of the barcode during scanning.
For example: UPC Code: 012345678905
012345 – Manufacturer Code
67890 – Product Code
5 – Check Digit
The barcode itself represents these digits visually with a series of vertical black bars and white spaces that scanners can interpret.
How Does UPC Work?
When a product with a UPC barcode is scanned:
A barcode scanner reads the black-and-white pattern.
The scanner converts the pattern into a 12-digit number.
The Point of Sale (POS) system retrieves the product details (e.g., name, price, inventory data) from a database.
The sale is processed, and the inventory system is updated.
This automated process eliminates the need for manual data entry, reduces errors, and speeds up checkout lines.
Benefits of Using UPC Codes
Improved Inventory Management: UPCs enable businesses to track stock levels accurately, minimizing the risk of overstocking or running out of products.
Faster Checkout Process: Scanning a UPC barcode is far quicker and more reliable than entering product information manually.
Global Compatibility: UPC codes are universally recognized, allowing seamless trade and distribution across international markets.
Error Reduction: Automation reduces the likelihood of pricing or data entry mistakes.
Better Sales Tracking: Retailers can analyze sales data more efficiently, identifying popular products and optimizing stock levels.
UPC vs. Other Barcode Systems
While UPC is widely used in North America, other barcode systems, such as EAN (European Article Number) and QR Codes (Quick Response Codes), are also common in other regions and applications.
UPC: Standard in the United States and Canada.
EAN: Widely used in Europe and other regions, with 13 digits instead of 12.
QR Codes: Store more data and are often used for mobile payments, marketing campaigns, and product authentication.
Despite the emergence of these alternatives, UPC remains the most common barcode standard in North America.
How to Get a UPC Code
To create a valid UPC for a product:
Register with GS1: Businesses must apply for a unique company prefix from GS1 US.
Assign Product Numbers: The manufacturer assigns unique numbers to each product.
Generate Barcodes: Using barcode generation software or services, the numeric codes are transformed into scannable barcodes.
Label Products: Print and affix the UPC barcodes on product packaging.
The Future of UPC
As technology advances, UPC codes are evolving alongside other retail technologies, such as RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) and smart packaging. However, UPC remains an integral part of global commerce. Innovations like 2D barcodes and QR codes are being integrated with UPC systems to enable more data storage and improve tracking capabilities.
Additionally, UPC codes are playing a key role in e-commerce platforms by ensuring accurate product identification across different online marketplaces.
Conclusion
The Universal Product Code (UPC) is a vital element in the global retail and supply chain infrastructure. By simplifying product identification, streamlining sales transactions, and enhancing inventory management, UPC has become an irreplaceable tool for businesses worldwide.
As retail continues to evolve with technological advancements, UPC remains a reliable and efficient solution for product tracking and data management. Whether you're a manufacturer, retailer, or consumer, the humble barcode on every product you buy continues to make modern commerce more efficient and connected.
0 notes
Text
Use Enhanced GS1 Barcode Generation & Recognition in SQL Server Reporting Services
What’s new in this release?
We are happy to announce the new release of Aspose.BarCode for Reporting Services 17.4.0. The major development in this release is the enhanced functionality of GS1 coded barcode. More often it is seem that GS1 code text contains complex combination of digits and letters. With Aspose.BarCode for SSRS 17.4, parsing and validation of those complex combinations is possible. Aspose.BarCode for SSRS allows developers to generate GS1 coded barcode according to AI (Application Identifier) specifications. New validators have been incorporated that can validate text code having only digits and complex AIs (combination of digits & letters). API will throw an exception in case it fails to validate. According to AI specification (ref: 703 AI, with letters – 324a, with more than 4 symbols) code text “(703)123” is incorrect. Aspose.BarCode will throw following exception if user tries to generate the barcode with EncodeTypes as GS1Code128. The following exception message will be displayed for such an incorrect barcode. Functionality of ExportToXml method has been improved. ExportToXml method now export dimension properties along with other properties of the newly define barcode into XML file. Below is the list of new and improved features added in this new release.
Improve GS1 parsing and validation
BarCodeBuilder allows to generate incorrect GS1 barcodes
Barcode generator accepts incorrect GS1 codetext
BarCodeBuilder.ExportToXml method is not exporting dimensions of the barcode in the XML file
Reorganize properties in Properties Window
Overview: Aspose.Report for .NET
Aspose.BarCode for Reporting Services is a .NET solution for the rendering of barcode images in SQL Server 2000, 2005 & 2008 Reporting Services. It supports 29+ linear (1D) and 2D barcode symbologies including MacroPdf417, Australia Post, OneCode, Code128, Code39, PDF417, UPCA, Codabar, MSI and QR etc. Also render barcode images on reports in BMP, JPG, PNG and GIF formats. Other features include EAN-128 application identifiers, DPI resolution settings, barcode size and location adjustments.
More about Aspose.Report for .NET
Homepage of Aspose.BarCode for Reporting Services
Download Aspose.BarCode for Reporting Services
Online documentation of Aspose.BarCode for Reporting Services
#GS1 Barcode Generation#GS1 Barcode Recognition#GS1 coded barcode support#GS1 barcode validation#export dimensions of barcode in XML#SQL Server Reporting Services
0 notes
Text
Barcode Registration by Indian Barcode Corporation (Mindwar

Barcode registration enables visibility on Google search for the barcode number affix on the product. On registration, Barcode scanning will return product information from an international database to the readers online. You can registered your Barcode here– https://www.indianbarcode.com/barcode-registration-services
Registered Barcode & Free Barcode - Registered barcode is that which helps prevent theft or accidental misuse of your barcode numbers, as you have extra proof that they belongs to you. If your barcode is registered on internet database, it can dissuade people from using the barcode number illegally on sites like amazon whereas you may use free barcodes as a part of your non-commercial web application or web-site.

Let’s discuss about the Advantages of barcode registration
Our barcode registration service is completely optional but however, there are several advantages to registering your barcodes:v Registration makes your product visible on some cell phone app scanners – Barcode registration helps with some cell phone app scanners (such as the Zebra app) so that when the product barcode is scanned the product information will appear.v Registration Increase the internet profile of your product – Barcode registration will increase the internet profile of the product so that when the barcode is searched for on Google or another search engine the product information will appear. This makes it easier for retailers and customers to find your company & product information.v Registration helps prevent theft or accidental misuse of your barcode numbers– as you have extra proof that they belong to you. If a barcode is registered on internet databases, it can dissuade people from using the barcode number illegally on sites like Amazon. If a quick internet search tells the person that the barcode number is in use they will be much less likely to use the barcode.v Registration helps prove that your barcodes are valid – Registration helps those few reluctant retailers who still think GS1’s database has all the answers, you can point them to this independent database where your barcodes are registered, as proof that they are yours, and are valid. This can save a lot of wasted time and unnecessary frustration with some retailers.It is easy to copy a barcode, anyone can see a barcode number and then duplicate that barcode on a different product. Our registration helps protect you against illegal use of your barcode numbers, and helps retailers and customers find the details of your product and business.
Now the question is How to register your barcode?
You can register your barcode and product or company details on https://www.indianbarcode.com/barcode-registration-services it will increase the profile of your product on the internet.After you register your barcode and product details, your product details will be displayed when customers search for your barcode number in online search engines (e.g. Google) or on some smart-phone apps (e.g. the Zebra app).
Now Let’s talk about How to get a Barcode?
The right procedure needs to be followed for the process of barcode registration. The steps involved in the process include:Ø Deciding on the type and number. The barcode is of various types and it can be taken in different lot sizes. The process begins with the identification of a requirement by the applicant.Ø Arrange documents. For barcode application, there are various documents like the balance sheet of the company’s bank account to prove the turnover of the company, etc. that need to be annexed.Ø Government fee. The Government fee is paid in the form of a demand draft after determining the lot size and the validity period of the barcode to be acquired.Over 2 million companies globally use barcodes, making it the default standard for the retail industry worldwide. Barcodes are a very efficient way to categorize and sell your products. Therefore, it is important to register your barcode. This will allow your barcode to be unique. If you are still wondering about the process of barcoding, Contact MINDWARE (Indian Barcode Corporation) as we provide you with the advantages of barcodes & assistance or guidance for Barcode registration and any queries related to it or to the business in general .
IS BARCODE REGISTRATION MANDATORY?
Barcode registration is not a government compulsory requirement. A retail barcode will work fine even without registration because stores enter the barcode number and link it to their billing or inventory software on an individual basis. .
Barcode Registration
Our (Indian Barcode Corporation) Barcode Packages allows you to register your product or Company details alongside the Barcode number in an online database. If require you can Contact us. Here is Our Contact number - +91 9810822688 you can also send mail to [email protected]

MINDWARE~ Oldest Company in India..Established in 1997
Address:- S-4, Plot-7, Pocket-7, Pankaj Plaza, Near Metro Station, Dwarka Sec-12, New Delhi, Delhi - 110078
Contact Mindware Today! +91 9810822688/8527522688
You can registered your Barcode here– https://www.indianbarcode.com/barcode-registration-services
#barcoderegistration#barcodes#eancodes#barcodesbymindware#registeryourbarcodes#indianbarcodes#mindware
0 notes
Text
GTIN and UPC
Understanding GTIN and UPC: Key Components of Product Identification
In the world of commerce, efficient product identification is critical for streamlining operations, reducing errors, and improving customer experiences. One of the most widely used systems for product identification is the GTIN (Global Trade Item Number), which includes the UPC (Universal Product Code) as one of its formats. Both the GTIN and UPC play an essential role in ensuring that products are easily identifiable across the supply chain, from manufacturing to retail.
What is GTIN?
The GTIN is a global identifier used to uniquely recognize products and services in the global supply chain. It is part of the Global Standards system, developed by GS1, to ensure consistent identification of products worldwide. The GTIN system includes several formats, such as GTIN-8, GTIN-12, GTIN-13, and GTIN-14, each serving different product categories and regions.
What is UPC?
The UPC is a specific type of GTIN—specifically, the GTIN-12 format used primarily in North America. UPC codes are 12 digits long and are typically represented in the form of a barcode. These barcodes are scanned in retail environments to quickly identify products, facilitating faster checkouts, inventory management, and order processing.
A UPC is composed of three parts:
Company Prefix: The first set of digits identifies the manufacturer or company responsible for the product. This prefix is assigned by GS1.
Product Code: The next set of digits represents a unique identifier for the specific product being sold.
Check Digit: The final digit is used to validate the accuracy of the UPC number, helping ensure that the barcode is read correctly by scanners.
How Does GTIN and UPC Work Together?
The GTIN and UPC work in tandem to ensure consistent product identification across different systems. While the UPC is a 12-digit identifier (GTIN-12), it is part of the larger GTIN system, which includes other formats like GTIN-13 and GTIN-14. Businesses can use different GTIN formats depending on the region and the type of product.
When a UPC barcode is scanned at a point of sale (POS), the UPC code is decoded, and the product details stored in the database (such as the product name, price, and stock quantity) are retrieved instantly. This allows for efficient checkout, inventory management, and order fulfillment processes.
Benefits of Using GTIN and UPC
Streamlined Transactions: UPC barcodes enable faster, more efficient transactions in retail environments. By simply scanning the barcode, employees can instantly access the product's details, speeding up the checkout process.
Accurate Inventory Management: GTIN and UPC codes help businesses maintain accurate inventory levels, making it easier to track product stock, reorder items when necessary, and avoid errors that can arise from manual data entry.
Global Product Recognition: As part of the GTIN system, the UPC is recognized across various industries worldwide. This ensures that products are easily identified and tracked, whether they're being sold in local retail stores or global e-commerce marketplaces.
Reduced Errors: Since GTINs and UPCs eliminate the need for manual product entry, they help reduce the risk of human error. This leads to more accurate orders, fewer stock discrepancies, and better overall customer satisfaction.
E-Commerce Integration: Many online marketplaces require GTINs (including UPCs) for product listings. Having a UPC for your product ensures that it can be listed on platforms like Amazon, eBay, and other global retail websites, allowing you to reach a broader audience.
How to Obtain a UPC
To obtain a UPC, businesses must register with GS1, the organization responsible for assigning GTINs. Once registered, businesses are given a unique company prefix, which is incorporated into each UPC code they create for their products. The UPC barcode can then be generated and placed on product packaging for easy scanning.
Resources like gtin.info offer valuable guidance on how to obtain GTINs, generate UPC barcodes, and integrate them into business operations.
Conclusion
The GTIN system, including the UPC code, is an essential tool for product identification in today’s retail and e-commerce environments. Whether you're managing inventory, processing sales, or expanding to international markets, understanding how GTINs and UPCs work can help streamline operations and improve efficiency. By using standardized product identification, businesses can ensure greater accuracy, reduce errors, and enhance the overall customer experience. For companies looking to implement GTINs or UPCs, resources like gtin.info provide the support and information needed to get started.
0 notes
Text
apply for barcode
To apply for a barcode, you need to follow a few steps to ensure that your product is properly identified and that you comply with international standards. Barcodes are essential for retail, inventory management, and distribution, as they make it easier to track and identify products throughout the supply chain.
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to apply for a barcode:
1. Register with GS1
GS1 is the global organization that manages barcode standards, including the UPC, EAN, and GTIN codes. To obtain a barcode, you will need to become a member of GS1. Follow these steps:
Visit the GS1 Website: Go to the official GS1 website for your country (such as GS1 US, GS1 UK, or GS1 International).
Create an Account: Sign up as a business and provide necessary details about your company.
Obtain a GS1 Company Prefix: Once registered, you will receive a unique GS1 Company Prefix. This prefix is part of the barcode and helps uniquely identify your business. The number of digits in the prefix depends on the number of products you plan to barcode.
2. Determine the Type of Barcode You Need
You’ll need to decide which type of barcode fits your business and the products you sell. The most common barcode types are:
UPC (Universal Product Code): Typically used in the United States and Canada for retail products.
EAN (European Article Number): Used primarily outside of North America, especially in Europe.
GTIN-12/GTIN-13/GTIN-14: These are global product identification numbers used to uniquely identify products across the supply chain.
QR Codes or Data Matrix Codes: These 2D barcodes are used for other purposes like marketing or on smaller products.
If you’re unsure which type of barcode to choose, consult with GS1 or review the requirements of your industry or retail partners.
3. Assign Product Numbers
Once you have your GS1 Company Prefix, you can begin assigning product numbers to your items. The product number is unique to each product and is combined with your GS1 Company Prefix to create a GTIN (Global Trade Item Number). This number will be embedded into the barcode.
For example, a UPC barcode has 12 digits: the first 6–10 digits represent your GS1 Company Prefix, and the remaining digits represent your product’s unique number. The last digit is a check digit that validates the barcode.
If you plan to barcode many products, it’s essential to have a system for assigning unique product numbers to each item.
4. Generate the Barcode
After assigning GTINs to your products, you will need to generate the actual barcode. This can be done using:
Barcode Software: Many barcode generation tools are available online that allow you to input your GTIN and generate the corresponding barcode.
GS1 Services: GS1 provides tools and services to help you generate barcodes based on your GTIN.
The barcode can be generated in different formats, such as UPC-A, EAN-13, or QR codes, depending on the type of product and application.
5. Print the Barcode
Once you’ve generated the barcode, you’ll need to print it onto your product packaging or labels. Ensure that the barcode is printed clearly and large enough for scanners to read easily. It is crucial to test the printed barcode to make sure it can be scanned without issues.
Barcode Printing Software: Use a reliable printing method to ensure the barcode is high quality. Many label printers are available for printing barcodes directly onto packaging.
Consider Placement: Place the barcode in an area that is easy to scan and not obstructed by other labels, packaging, or designs.
6. Verify the Barcode
Before distributing your products or listing them for sale, it’s essential to test your barcode using a barcode scanner to ensure it is scannable. You can use a handheld scanner or a smartphone with barcode scanning software to check that the barcode is correctly linked to the product information.
7. Maintain Barcode Records
It’s essential to keep accurate records of your GTINs and associated products. This will help you track inventory, manage sales, and update product information as necessary. Most businesses use barcode management software or inventory systems that integrate with the barcode.
8. Use Your Barcode in Retail
Once your barcode is generated, printed, and verified, you’re ready to use it in retail environments, both physical and online. Online marketplaces such as Amazon, eBay, and Walmart require sellers to use barcodes for product listings. Make sure your barcodes are properly registered and linked to your product information in retail systems.
Conclusion
Applying for a barcode is a relatively straightforward process but requires careful planning and attention to detail. By registering with GS1, obtaining a unique Company Prefix, and following the steps to generate and print your barcode, you can efficiently track and sell products both in physical stores and online.
Barcodes are essential for improving inventory management, speeding up transactions, and ensuring accurate product identification. Whether you're a small business or a large enterprise, getting your products properly barcoded will help streamline your operations and ensure you comply with global standards.
0 notes
Text
Food Traceability Market - Forecast(2022 - 2027)
Food Traceability
market is expected to reach $18,528 million by 2023, registering a CAGR of 9.1% from 2018-2023. Food traceability comprise the ability to identify and validate various stages of food chain from production to distribution. It involves recognizing the origin of food and its destination, from where it will be distributed to end users. This system is essential for food investigations and is crucial in global food trade as multi ingredient food includes materials from variety of food chain and countries.
What is Food Traceability Market?
Food traceability system maintains the record of the flow of products which are actually meant for human consumption throughout the production process. Since food production and the distribution is a complex process the companies consider food traceability system as the best tool to solve all the food-related challenges. Food traceability helps the companies to make fresh food products available to their consumers, thereby helping in reducing food-borne diseases. In many countries, such as the US and UK, consumers are ready to pay more for products having a food traceability and point-of-origin certificate. Technologies such as infrared, RFID, biometrics, barcode, NFC and sensors have made food traceability convenient for companies in the food industry.
As food production consists of various stages, including sourcing seeds & fertilizers, farming, harvesting, processing, storage, transportation and retail sales, there are risks associated in it such as contamination, making it imperative to have a food traceability system. The procedures involved during this process include identification, link, records of information, collection & storage of information and verification.
What are the major applications for Food Traceability market?
The various end users assessed includes Food manufacturers, Warehouse/Pack farms, Food retailers, Defense and security departments and other Government departments. Food traceability market in retailers are used to achieve internal and external traceability. Internal traceability allows the company to follow the product through the system after receiving the receipt from the supplier whereas the external traceability allows for the connection with immediate supply chain partner.
Market Research and Market Trends of Food Traceability Nitride Ecosystem
Companies are investing in research and developing new hardware and software tracing technologies like GS1-128 barcode which as the capability to capture more traceable data such as batch number, lot number, sell by date, Use date. The Company have to make sure that all DCs in their supply chain are capturing and storing all the dynamic information carried in the bar code.
Another prevailing trend in the food tracing industry would be digital supply chain in which technologies like predictive analytics, better visibility over the movement of goods and robotics help the warehouse and distribution centers to trace food efficiently.
Warehouse managers have designed a warehouse management system with radio frequency guns restricting the person to pick a wrong product. In case the person picks up a wrong product, a specially designed gun gives a beep indicating wrong product is picked up.
The transportation management system would be digitized which was handled manually initially. This is achieved by using the systems own parameters, standards, data points and expectations, the retailers can give its suppliers specific delivery time frames using cloud based interconnected solution. This will not only streamlined the scheduling process, but it will also give the tremendous amount of tracking information and data that we don’t have before.
Who are the Major Players in Food tracing system?
The companies referred in the market research report includes Honeywell International Inc, C.H. Robinson INC, Dupoint Nutrition & Health, Intermec Inc, Motorola solutions, Cognex Corporation, MASS Group, Bio-Rad Laboratories, IBM Corp, Zebra Technologies and more than 10 other companies.
What is our report scope?
The report incorporates in-depth assessment of the competitive landscape, product market sizing, product benchmarking, market trends, product developments, financial analysis, strategic analysis and so on to gauge the impact forces and potential opportunities of the market. Apart from this the report also includes a study of major developments in the market such as product launches, agreements, acquisitions, collaborations, mergers and so on to comprehend the prevailing market dynamics at present and its impact during the forecast period 2018-2024.
All our reports are customizable to your company needs to a certain extent, we do provide 20 free consulting hours along with purchase of each report, and this will allow you to request any additional data to customize the report to your needs.
Key Takeaways from this Report
Evaluate market potential through analyzing growth rates (CAGR %), Volume (Units) and Value ($M) data given at country level – for product types, end use applications and by different industry verticals.
Understand the different dynamics influencing the market – key driving factors, challenges and hidden opportunities.
Get in-depth insights on your competitor performance – market shares, strategies, financial benchmarking, product benchmarking, SWOT and more.
Analyze the sales and distribution channels across key geographies to improve top-line revenues.
Understand the industry supply chain with a deep-dive on the value augmentation at each step, in order to optimize value and bring efficiencies in your processes.
Get a quick outlook on the market entropy – M&A’s, deals, partnerships, product launches of all key players for the past 4 years.
Evaluate the supply-demand gaps, import-export statistics and regulatory landscape for more than top 20 countries globally for the market.
#Food Traceability Market share Food Traceability Market#Food Traceability Market size Food Traceability Market
0 notes
Text
What is a Universal Product Code (UPC)? - Types, Decoding



You've probably seen those barcodes with all the lines and squares on them, but what are they, and what do they do? They are Universal Product Codes. They track products through the supply chain. They're scanned at each point of sale to ensure that the correct product is being sold. It is a barcode symbology widely used in the United States and other countries. It consists of 12 digits that uniquely identify a product. You can find this code on most products that you buy in stores. This blog post discusses the definition, symbology, types, advantages, disadvantages, and requirements of UPC. In addition, the post explains the steps to get UPC for your product.
Definition
A Universal Product Code is a unique code assigned to every item sold in the store. The code helps identify the product, store traffic trends, and inventory details. That helps further in maintaining complete ordering information for the business. It provides real-time data to the store or the supermarket to ensure they never run out of stock for fast-moving items. It also makes the billing system easy and swift. UPC-E (includes zero) and UPC-A (does not have zero) are the two main types of Universal Product Codes.
UPC Symbology

It is made up of four parts: - The number system identifies the type of product; - The manufacturer code, which UCC Council assigns to a specific company; - A unique item identifier or SKU, which is posted by the manufacturer for each product they make; and, - A check digit is calculated using a special algorithm to ensure a valid code. The first digit indicates the product type, and the following five digits are a unique code provided to the vendor. Thus, the vendor will have the same code even if the store differs. The following five digits act as the unique reference specified for the product, and the last digit will be the check digit which is generally used to cross-check if it is correct. It is scanned against a scanner that reads the bar code and lets the system know if everything is okay or not.
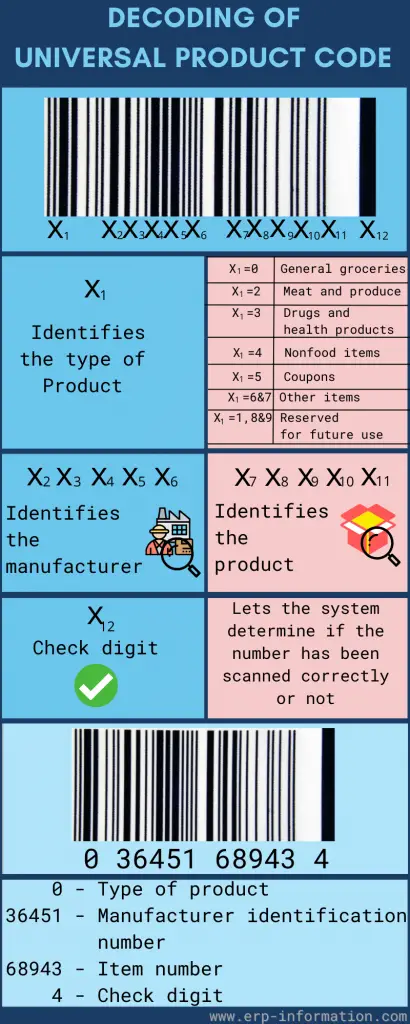
Steps to Get UPC Code for a Product
Application filling The first step is to get the GS1(Global Standard Organization), also known as the Unifor Code Council company prefix. For that, you have to fill out the online application form and sign up for a prefix capacity plan to get it. It shows the number of universal product codes under your company prefix. Paying Fee You have to pay the fee for the code. A prefix capacity plan can be expensive. So make sure that the plan you have chosen will accommodate the long-term use of your business. Once you pay the fee, GS1 allocates a 6-digit number with the manufacturer identification number. This number becomes the first six digits of the universal product code on your company's products. Internal product number generation After getting your company prefix, you can give your product internal product numbers (5 digits). You have the freedom to choose your digits, but each product should have a unique UPC. Ensure that the exact number is not used for more than one product. This 5-digit number represents the product itself. Check digit generation After generating your company prefix and internal product code, generate your check digit. It generates after several calculations by adding and multiplying digits in the code based on an algorithm monitored by the global standard organization(GS1). Manually also, you can calculate the check digit. Confirm check digit is correct or not. If the check digit is incorrect, the UPC code will not scan properly. Registration of final barcode Once all three sets of digits, company prefix, internal product code, and check code are generated, register this number with GS1 so that you will tie your product information to the number you have created. The below infographic provides summarized information on UPC barcode generation steps.

UPC Code's Location
They can be found in most products that you buy in stores. The code is usually located somewhere on the product packaging, and you may also print it on the product. They are also found in product manuals, promotional materials, and shipping boxes.
How to Find a Manufacturer's UPC?
Suppose you want to find the Universal Product Code for a specific product. There are several ways to do so. You can visit the manufacturer's website or contact them directly to ask for the code. You can also use a UPC lookup tool to find the code. These tools are widely available online, and they are free to use. When using a lookup tool, you need the product's name or SKU number. You can usually find the SKU number on the product packaging or manual. Once you have entered the information into the lookup tool, it will return the Universal Product Code for that product. UPC Lookup Tools These tools allow you to search for product codes by keyword or browse by category. They also provide information about the product, such as the manufacturer's name, address, photos, and descriptions. Some tools even let you add products to your inventory. One example is GSOne Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) Database.
Types of UPCs

There are a few different types of Universal Product Codes. The most common type is the 12-digit code used to track store products. Codes can also be 6 or 9 digits long. The 6-digit code is used to track products sold in vending machines, and the 9-digit code is used to track online products.
Universal Product Code Generator
A Universal Product Code Generator is a tool that allows you to create Universal Product Codes for your products. This tool is helpful if you want to make your barcodes for tracking purposes or if you want to include them on your product packaging. There are several generators available online. Most of these tools are free to use and easy to use. You need to enter the information about your product, such as the name and SKU number, and the generator will create a valid code for you.
UPC Barcode Specifications
The Universal Product Code Barcode Specifications are guidelines that describe how they should be formatted and used. These specifications are maintained by the Universal Code Council (UCC), a nonprofit organization that oversees the system. The specifications define the following: - The structure and format - The type of information that can be encoded - How it should be scanned and read - They use it in retail environments - They use it in other industries The UPC barcode Specifications are essential for businesses to create or use barcodes. By following the guidelines in these specifications, companies can ensure that their barcodes will be compatible with scanning equipment and that they will be readable in retail stores.
UPC Code Requirements
To create a barcode, you must encode the product's name or SKU number into a barcode format. There are some free online tools that you can use to do this. Once you have created the barcode, you can print it out and attach it to your packaging. Retail scanners scan and read codes, automatically entering the product information into the store's database. This allows businesses to track their inventory and sales without manually entering the information into their database.
Advantages
- They are easy to use and can be scanned by retail scanners. - They speed up the checkout process in stores. - They help businesses track their inventory and sales. - They can be used to create marketing materials such as flyers and product labels. - They are a global standard and are accepted in most countries.
Disadvantages
- Barcodes can be expensive to create and print. - They are not always accepted in all countries. - They can be challenging to create without using a barcode generator tool. - They may not be suitable for all products or businesses. - They require special scanning equipment to read them correctly.
FAQs
How many types of bar codes are there? There are three types of bar codes. They are 1. Universal Product Code (UPC) 2. International Article Number (IAN) 3. International Standard Book Number (ISBN).What is EANEAN stands for European Article Number, also known as International Article Number. It is an international standard for identifying products and services within the EU and elsewhere. In 2009, 13-digit Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) replaced EAN. EAN-13 is the most commonly used 13-digit EAN standard. What are the differences between UPC and EAN?The differences are as follows. EAN is used mainly in Europe, while UPC is primarily used in the United States. EAN codes have 13 digits, while UPCs have only 12 digits. Furthermore, EANs are encoded to contain information about the product's country or region of origin. In contrast, UPCs do not include this information because they are only used in the US and Canada.
Conclusion
In this post, you learned what Universal Product Codes are and how businesses can use them. You also learned about their advantages and disadvantages of them. We hope the article provided quality information. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Procedure for barcode registration in Vietnam
For a long time, consumers are used to the image of barcodes or the black and white lines or square matrix codes on products. These images, though simple, contain a great amount of information as well as contribution to helping many retailers easily arrange, store and search for product information. Because of its great benefits, barcode registration for goods is received a lot of attention from business subjects. Therefore to meet the needs of our clients, Apolo Lawyers (Tel: (+84) 903.419.479) provides the legal consultation service on barcode registration in Vietnam, which helps you to complete the procedure for barcode registration for goods fastly and efficiently.

1. What are barcodes and barcode registration?
Barcode is the combination of white spaces and white bars arranged according to the rules and parameters, which can only be read by specialized devices such as scanners. Barcode is a method to store and transport the information, data of products, goods,… encoded using a combination of spaces and dashes to represent letters, symbols, and numbers.
Barcode registration is when organizations or individuals prepare dossiers and register at the Ministry of science and technology of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam to be granted the certificate of barcode registration. Therefore, organizations and individuals can bring barcodes to print on their products to use.
2. How to register a barcode?
Vietnamese Law does not require business entities to conduct the procedure for barcode registration, but it encourages them to do this to expand markets and develop businesses and the economy of the country. The procedure for barcode registration will be implemented according to these steps:
Step 1: Determine the number of products needed to be registered with barcodes
There are three types of barcodes:
Less than 100 products;
Less than 1000 products;
Less than 10.000 products.
Depending on the number of products that clients want to register barcode, client could choose a suitable barcode package.
Step 2: Prepare barcode registration dossier
The application for barcode registration includes:
Registration form of use of codes and barcodes;
A copy of the business registration certificate or establishment decision;
Registration form of the product catalog using the GTIN code;
Registration form for GS1 Vietnam database.
Step 3: Register the dossier to the Ministry of science and technology of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam.
Step 4: The registry examines the application for registration of barcode
After submission, the dossier of barcode registration will be appraised at the Registra from 5 – 7 working – days.
Step 5: Granting a barcode and certificate of registration for the enterprises
After verifying the registration documents and confirming the complete and valid documents, the registration agency will issue the barcode to the enterprise for use first, and the barcode registration certificate will be issued to the registrar. Signed then about 30 days.
>>> Read more: Conditions for the protection of industrial designs

3. Legal service for barcode registration for goods in Vietnam at Apolo Lawyers
Proud to be a law firm with many years of experience, Apolo Lawyers committees to provide our clients no limitations, but this support:
Consulting on choosing the type of barcodes that are suitable to the size and intentions of the Enterprise.
Consulting on the selection of barcodes film master in accordance with the product characteristics of the enterprise.
Consulting and completing the application for barcode registration.
Support Enterprises to implement the Ministry of science and technology of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam used to register barcodes.
Submit an application for a barcode certificate at the General Department of Standards, Metrology, and Quality. Monitor the progress of case processing. Receive MSMV film master and transfer to Enterprise for printing and use.
Consulting and supporting businesses in the entire process of using barcodes.
For further information, please contact us: Apolo Lawyers
APOLO LAWYERS
#barcode#barcode registration#what are barcodes#how to register a barcode#legal service for barcode registration
0 notes
Photo

UPC Barcode an Overview
UPC barcode numbers are not picked at random by a brand owner, but rather a string of digits that correspond to a global standard that allows items to be sold globally. The UPC barcodes are basically for the product barcode. To assure validity and prevent duplicate UPC barcodes from being allocated, the data in a UPC barcode must include a UPC (GS1) Company Prefix assigned by GS1 to a specific brand, an Item Reference Number assigned by the brand owner, and a mathematically generated Check Digit. A firm must first apply to become a member of the system in order to get a UPC for use on a product.
0 notes
Photo

Global Trade Item Number - GTIN
An individual number with international validity that serves to identify products or for look up product information in a database.
In principle, this serves to identify products and services worldwide without overlap by referring to business information stored in computer files – such as prices, conditions, suppliers, designations, product groupings or special numbering.
This is used wherever products that can be automatically recorded and processed need to be marked. As a rule, this is always made up of 13 purely numerical digits. It represents the new standard in product marking since it replaced the previously common EAN (European Article Number) in 2009.
It refers to all levels of packing which could be purchased and maintained in an inventory system. This includes individual items which can be purchased by a consumer, as well as cases of items that could be purchased by a retailer and moved within their supply chain.
In short, it is an umbrella term used to refer to items and cases which may need to be identified with a GTIN barcode. It is an identifier for trade items administered and assigned worldwide by GS1 (Global Standards One).
#fresa #freightsolutions #freightforwarding #import #GlobalTradeItemNumber #billoflading #vessel #GTIN #bestfreightforwardingsoftware #pallet #export
1 note
·
View note
Text
PRISYM 360 SaaS Labeling Solution Offers Validated Platform for COVID-19 Clinical Trials

PRISYM 360 SaaS Labeling Solution Offers an Instant Validated Platform for COVID-19 Clinical Trials Wokingham, United Kingdom — 8th April 2020 — PRISYM ID, a leading provider of data-led label and artwork management solutions today announced its PRISYM 360 SaaS clinical trials labeling solution is live with customers and available to those pharmaceutical and trials organizations who need quick entry to clinical label printing.
To support the life sciences sector’s response to Covid-19, PRISYM ID is offering a cloud-based, ready to use version of its clinical trials SaaS labeling platform including a pre-validated pack with industry standard print processes. It is fast to onboard, needs minimal IT input to set up and provides certainty to the market in these uncharted times.
Being pre-validated, the application removes a significant proportion of the cost, time and risk associated with implementing and validating a labeling system. It provides organizations with the control and agility needed to remove risk for clinical trial printing processes. Key features of this version include:
Role based security controls
Printer agnostic label designs
Clinical trial filtered study and sequenced printing (Clinical Trial Supply)
Product label printing
Comprehensive, secure audit log including the ability to transfer content and templates to different organizations as the trial grows
Language management controls
Version and state control of all design and content elements
Version and state control of data models and workflows
Workflow templates
Clinical trial data management, including the import and management of randomized data
Extensive barcode symbology support, including GS1 Clinical Trials
Hosted through a fully validated and compliant cloud environment
Warren Stacey, SVP of Sales at PRISYM ID, commented: “With the life science industry working at exceptional speed to run trials and accelerate the speed at which they come to market, labeling may be something of an afterthought. Yet it is critical to the process. Generic labeling software may be a blunt tool when it comes to validation, version control, compliance and navigating the nuances of the clinical trials supply chain. Our PRISYM 360 SaaS solution already has customers live in this space and it offers clinical researchers an off-the-shelf platform that’s fit for purpose, validated and secure.”
ends
Note to Editors: PRISYM ID designs and delivers label management software for organizations that need complete product auto identification and lifecycle traceability. With the continual tightening of labeling regulations and audits, PRISYM ID empowers its clients to safeguard their reputation by ensuring compliance, removing risk and significantly reduce costs by eliminating recalls through labeling errors. PRISYM ID is the market leader in providing validatable world-class label lifecycle management and is trusted for delivering personalized service excellence to clients. www.prisymid.com
For more information:
Andrew Baud, Distil, [email protected], +44 (0) 7775 715775
The post PRISYM 360 SaaS Labeling Solution Offers Validated Platform for COVID-19 Clinical Trials appeared first on .
from https://pharmaphorum.com/partner-content/prisym-360-saas-labeling-solution-offers-validated-platform-for-covid-19-clinical-trials/
0 notes
Text
New Post has been published on Vivan Life Sciences
New Post has been published on https://www.blog.vivanls.com/soon-iveda-portal-to-be-launched-to-track-drugs-for-export/
Soon iVEDA Portal to be launched to track drugs for export !

The central government will soon launch Integrated Validation of Exports of Drugs from India and its Authentication (iVEDA) portal for drug authentication and tracking and tracing of the drug supply.
iVEDA portal developed by the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) will replace Drugs Authentication and Verification Application (DAVA) portal which has hit technical glitches hampering manufacturers and exporters from uploading data on barcode on secondary and tertiary packs of drugs meant for export and maintenance of parent-child relationship between them.
Taking serious note of this, Director General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) had postponed the date for implementation of track and trace system for export of drug formulations with respect to maintaining the parent-child relationship in secondary and tertiary packaging levels and its uploading on the central portal till March 31, 2020. However, the requirement of bar-coding on secondary and tertiary packaging continues as per earlier notifications.
Having taken cognizance of the issues and concerns raised by the pharma industry with regards to trace and track and with specific reference to data upload issues on DAVA portal, the department of commerce constituted an expert committee. The recommendations arrived after series of consultations with the all the stakeholders led to the decision of developing a new web portal for validation and authentication of drugs export from India.
With the iVEDA portal being rolled out by third week of March, 2020, the manufacturers and exporters are required to upload data on barcode on secondary and tertiary packaging of drugs meant for export on the portal. Maintaining parent-child relationship between secondary and tertiary packaging is an optional.
The manufacturer uploading data on the central portal must have manufacturer code and product code allotted by GS1 India. The manufacturer can get CDAC codes in case he has not yet subscribed to get codes from GS1 or any other agencies. The manufacturer must have Digital Signature Certificate of Class-II or Class-III issued by any Certifying Authority (CA) in India.
The responsibility of the correctness, completeness and ensuring timely upload of data on the central portal shall be with the manufacturer. However, the manufacturer may extend the responsibility to anyone next to it in its supply chain i.e. wholesalers/ distributors/ retailers etc. in its supply chain.
The online system is envisaged to help manufacturers and merchant exporters to generate and utilise tertiary and secondary level coded data in a user-friendly manner. It has the provision to upload product and production data.
The test run workshop on iVEDA portal was held by Pharmexcil in Mumbai, Ahmedabad, Hyderabad, Chandigarh on February 10, February 11, March 3, March 5 respectively. The workshop was attended by manufacturer-exporters, merchant exporters, contract manufacturer exporters etc. The objective of the workshop was to provide industry hands-on experience and get their feedback to make the portal more robust, and industry friendly.
The industry has appreciated the portal.
Said Nipun Jain, Chairman, SME Panel, Pharmexcil, “The portal is industry friendly. With this portal, the challenges faced the industry while uploading data on the central portal have been resolved. The trial run of iVEDA will help industry well-versed with the portal before its launch.”
Said Uday Bhaskar, direector general of Pharmexcil, “We wanted to make the portal industry friendly and simplified and in this process, we are designing the programme of the portal with CDAC. We have taken all concerns of the industry including merchant exporters into the consideration.”
“The exporters who were earlier working with GS1 code are not required to change the entire system. They can continue with data uploading on the portal with minor changes. Those who did not have GS1 code can also upload data,” he added.
Reference: Pharmabiz
0 notes